Plastic forming is a method of designing, manufacturing, and assembling a product that is made from plastic. Plastic material is used in various ways in our daily life, and the plastic industry is growing daily. According to experts, plastic production may continue to grow and reach 540 million metric tons by 2040. Read More…
Valk’s policy is “to meet or exceed our customer’s requirements, working together as a team with honesty and integrity.” Valk’s success is due to their long standing focus on quality & customer service.

Since 1960, Profile Plastics Inc. has been at the forefront of thermoforming technology. Utilizing the latest software and technology, our expert staff of engineers can design custom vacuum, pressure, and twin-sheet thermoformed solutions. Over the last 60 years, we have developed a process that allows us to deliver consistent, high volume, and precise products with superior quality. Our high...
Quality Plastics has been a leading manufacturer of vacuum forming since 1976. Whether you need a small batch of custom vacuum-formed parts or a large-scale production run, we have the capabilities and expertise to deliver. We are committed to providing our customers with exceptional vacuum-formed products and services that meet their needs and exceed their expectations. Contact us today to learn ...

At Arrowhead Plastic Engineering, Inc., we’ve been delivering high-quality vacuum forming solutions since 1972. From concept to production, Arrowhead is with you every step of the way. We can use your 3D CAD model to CNC cut your pattern in house or we can hand sculpt your pattern if a 3D CAD model isn’t available.

Engineered Plastic Products custom forms & fabricates sheet thermoplastic materials, standard & specialized, for any number of industrial & commercial requirements. EPP has been widely recognized for outstanding manufacturing & service since 1958 for companies such as GE, NASA & AT&T. Custom fabricated parts can be as large as 72"x108" down to 2"x2" in any thickness up to 1 1/2". Post-forming...

Brisar Delvco Industries, Inc., specializes in delivering high-quality Thermo & Vacuum forming solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of our clients across a broad spectrum of industries. ISO9001, ISO13485, FDA Registered for Food, Medical Devices & OTC products. In house CNC tooling for quick prototype design, production tools and Thermoformed parts.

At Duo Form, we are pioneers in the realm of vacuum-formed plastic products. With a collective passion for precision engineering and creative problem-solving, we've established ourselves as leaders in delivering high-quality solutions to a wide range of industries.
At Hi-Rel Plastics & Molding, we specialize in precision vacuum forming and thermoforming solutions tailored to meet the unique demands of a wide range of industries. With decades of hands-on experience, we’ve refined our process to deliver high-quality, custom-formed plastic components that meet exacting tolerances and performance standards.

Robinson Industries offers thermoformed and injection molded reusable, heavy duty plastic pallets, packaging and more. We are one of the largest suppliers of reusable pallets to many industries.

More Plastic Forming Companies
Comprehensive Guide to Plastic Forming: Processes, Applications, and Choosing a Manufacturing Partner
Plastic forming is a core technique in plastic manufacturing, encompassing the designing, engineering, and assembly of products made from polymer-based materials. As the demand for durable, cost-effective, and versatile products grows, plastic forming processes have become integral to the production of countless everyday items. According to industry experts, global plastic production is projected to reach 540 million metric tons by 2040, reflecting the expanding role of plastics in sectors such as consumer goods, electronics, automotive, medical devices, packaging, and industrial equipment.
From kitchen utensils and wardrobe accessories to sophisticated electronic components and automotive assemblies, plastic is a cornerstone material driving innovation and efficiency across industries. Understanding the fundamentals of plastic forming, key properties, manufacturing methods, and how to select the right plastic forming company is essential for businesses and individuals seeking reliable, quality plastic products or custom plastic fabrication services.

Core Properties of Plastics
- Lightweight and Moldable: Plastics are significantly lighter than most metals, making them ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical. Their high plasticity allows for easy molding into complex shapes and sizes using various plastics processing techniques.
- Chemical Stability and Corrosion Resistance: Most plastics are rust-proof and resist degradation from a wide range of chemicals, making them suitable for harsh environments and chemical storage solutions.
- Electrical and Thermal Insulation: Plastics have low thermal conductivity and excellent insulating properties, making them indispensable in electrical housings, circuit boards, and construction insulation.
- Transparency and Versatility: Certain plastics like acrylic and polycarbonate can be manufactured with high optical clarity, useful for glazing, lenses, and displays.
- Cost-Effectiveness and Ease of Processing: Compared to metals and ceramics, plastics are generally low-cost and require less energy-intensive processing, especially for high-volume production runs.
- Poor Dimensional Stability: While easy to form, some plastics exhibit dimensional changes under varying temperature and humidity, which must be considered in product design.
Types of Plastic Materials
When researching which plastic materials are suitable for your project, it's important to understand the main categories and their unique properties. The two fundamental types of plastics are:
-
Thermosetting Plastics
Thermosetting plastics, or thermosets, undergo a chemical change during processing that permanently "sets" their shape. Once cured through heat, they cannot be remelted or reshaped. These materials exhibit high temperature resistance and strong structural integrity, making them ideal for electrical insulators, adhesives, and automotive components. Common examples include epoxy resins, phenolic resin, melamine, rubber, and polyurethane.
- Applications: Circuit boards, appliance housings, adhesives, automotive body panels, and kitchenware handles.
-
Thermoplastics
Thermoplastics can be repeatedly heated, melted, and re-molded without altering their fundamental chemical structure. This recyclability and ease of processing make them the most common plastics used in mass production. Examples include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), acrylic (PMMA), nylon (PA), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
- Applications: Bottles, packaging films, automotive parts, medical devices, household goods, and toys.
Plastic Forming and Manufacturing Processes
The plastic forming industry employs a variety of plastic fabrication methods to meet the diverse needs of product designers, engineers, and manufacturers. Each plastic forming process has unique benefits, tolerances, and cost considerations. When evaluating which technique is best for your part or product, consider the production volume, material specifications, and end-use requirements.
Plastic Injection Molding
- Injection molding involves forcing molten plastic pellets into a precision-machined mold (typically steel or aluminum) under high pressure.
- This process is highly versatile and suitable for producing complex shapes with tight tolerances, excellent surface finish, and high repeatability.
- About 80% of mass-produced plastic products, from bottle caps to automotive dashboards, are made using injection molding.
- Key advantages include scalability for large production runs, low per-unit cost, and the ability to use a wide range of thermoplastics and thermosets.
- Considerations include high upfront tooling costs and the need for regular mold maintenance to prevent defects.

Common Applications of Injection Molding
- Automotive components (dashboards, bumpers)
- Medical devices (syringes, housings)
- Consumer electronics (enclosures, connectors)
- Household products (containers, toys)
Rotational Molding (Rotomolding)
- Rotational molding uses powdered plastic loaded into a hollow mold, which is heated and rotated along two axes, allowing the plastic to coat the interior walls evenly.
- This process is ideal for producing large, hollow, and seamless parts such as tanks, playground equipment, and marine buoys.
- Rotomolding offers low tooling costs, excellent stress distribution, and the ability to create double-walled parts or complex geometries.
- It’s best for low to medium production volumes and parts where uniform wall thickness is essential.

Typical Products Made with Rotational Molding
- Storage tanks (industrial, agricultural, chemical)
- Outdoor furniture and play structures
- KAYAKS, canoes, and marine floats
- Bins, containers, and traffic barriers
Extrusion Blow Molding
- Extrusion blow molding is a high-speed process where molten plastic is extruded as a tube (parison), then clamped in a mold, inflated with air, and cooled to form hollow objects.
- This technique is widely used for manufacturing bottles, jars, and thin-walled containers for the packaging industry.
- It’s favored for its efficiency, low tooling costs, and capability for making disposable products or specialty packaging.

Extrusion Blow Molding Use Cases
- Plastic beverage bottles (water, juice, soda)
- Detergent, oil, and chemical containers
- Personal care packaging (shampoo, lotion bottles)
Injection Blow Molding
- Injection blow molding combines injection molding and blow molding, resulting in high-quality, dimensionally accurate hollow parts.
- Molten plastic is injection molded onto a core pin, then transferred to a blow mold where air expands the plastic to the final shape.
- This process is best for small to medium-sized bottles, especially where clarity and precise neck finishes are required.
Common Injection Blow Molded Products
- Pharmaceutical and cosmetic bottles
- Laboratory vials and dropper bottles
- Travel-sized and specialty packaging
Reaction Injection Molding (RIM)
- RIM uses two liquid components mixed and injected into a mold, where they chemically react and cure, forming lightweight, rigid, or flexible parts.
- Commonly used in the automotive industry for bumpers, instrument panels, and body panels where impact resistance and lightweight are desired.
- RIM can also produce foam-like structures with excellent surface quality and design flexibility.
- Tooling costs are higher, but the process supports large, complex, low-volume parts.
RIM Applications
- Automotive bumpers, fenders, and spoilers
- Medical equipment enclosures
- Industrial machine housings
Vacuum Casting
- Vacuum casting is used for prototyping and low-volume production, involving a master model and silicone or urethane molds filled under vacuum.
- It enables fast turnaround of high-fidelity parts, ideal for market testing, product development, and short runs.
- Materials can mimic the properties of engineering plastics, rubber, or elastomers.
- Note: Silicone molds degrade after a limited number of copies (typically 20–30).

Vacuum Casting Use Cases
- Prototypes for functional or aesthetic testing
- Short-run production for market validation
- Medical device housings and automotive interior parts
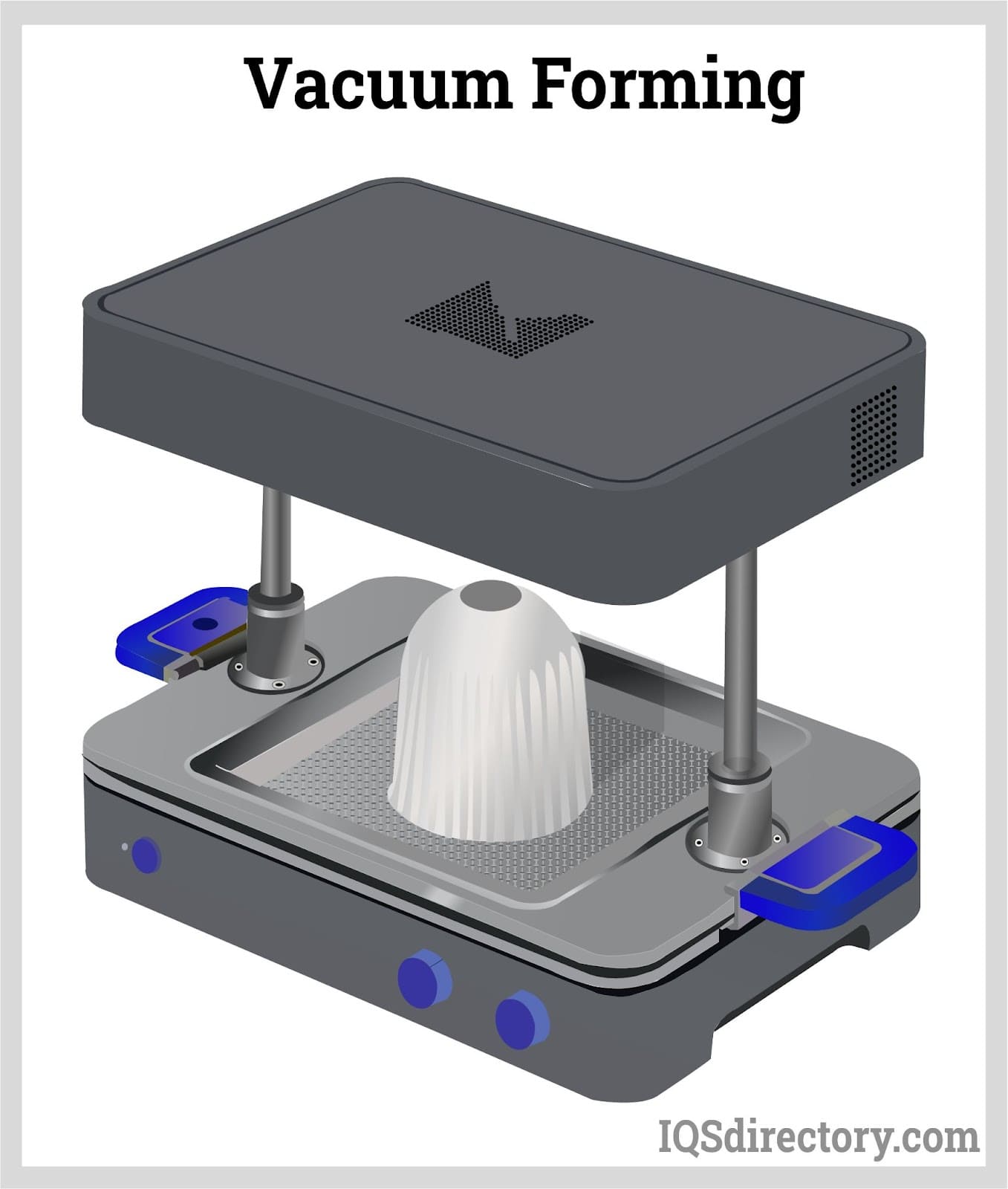
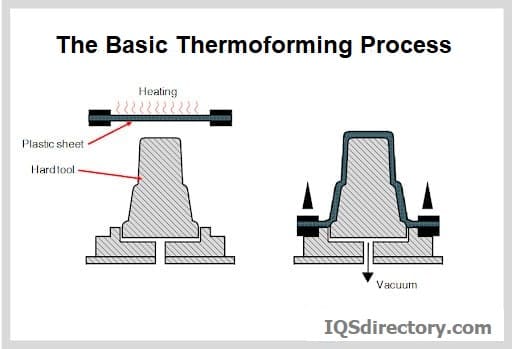
Thermoforming
- Thermoforming involves heating a plastic sheet until pliable, then forming it over a mold using vacuum or pressure.
- It’s an efficient technique for producing large, thin-walled, or shallow parts such as trays, packaging, and signage.
- Thermoforming can be categorized into vacuum forming and pressure forming, each offering unique benefits for different applications.
- Learn more about thermoforming and its advantages here.
Popular Thermoformed Products
- Plastic packaging (clamshells, blisters)
- Disposable cups, lids, and trays
- Automotive interior panels
- Medical device trays and enclosures
Compression Molding
- Compression molding is primarily used with thermoset plastics, where pre-heated material is placed in a heated mold cavity and compressed until cured.
- This method is suitable for producing strong, durable parts with excellent dimensional stability, such as electrical insulators, appliance handles, and automotive gaskets.
- It supports both low and high-volume production, with relatively lower tooling costs than injection molding.

Key Compression Molded Products
- Rubber keypad switches and gaskets
- O-rings and seals
- Electrical switchgear and insulation parts
Applications of Plastic Forming in Industry
Plastics' versatility and wide range of properties have driven their adoption in almost every industry. Here are some of the most common and high-impact uses of plastic materials and plastic-formed products:
- Consumer Goods: From furniture (chairs, tables) and appliances to toys and sports equipment, plastics offer lightweight, durable, and affordable solutions.
- Electronics: Plastic enclosures, circuit boards, cable insulation, and connectors rely on plastics' insulating properties and design flexibility.
- Medical Devices: Sterile syringes, diagnostic equipment, surgical instruments, and medical packaging leverage plastics' biocompatibility and ease of sterilization.
- Automotive and Aerospace: Lightweight dashboards, bumpers, panels, fluid reservoirs, and even aircraft interiors benefit from plastics' strength-to-weight ratio and recyclability.
- Packaging: Food packaging, containers, bottles, and clamshells protect products, extend shelf life, and offer design versatility for branding.
- Construction: Pipes, insulation, cladding, windows, and water tanks are made with plastics for their durability, weather resistance, and low maintenance.
- Industrial Equipment: Machine guards, gears, seals, and custom housings are formed from engineered plastics for their performance and chemical resistance.
- Safety and Protective Gear: Helmets, face shields, and children’s safety products are manufactured from impact-resistant plastics.

How to Choose the Right Plastic Forming Company
Choosing the best plastic forming company is crucial for ensuring the quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of your products. Whether you need custom parts for a new invention, specialized packaging, or mass production for retail, the right manufacturer will have the expertise, equipment, and materials to meet your needs.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Plastic Forming Manufacturer
- Technical Capabilities: Does the company offer the specific plastic forming process (injection molding, thermoforming, blow molding, etc.) that matches your part requirements?
- Material Selection: Can they work with the type of plastic (thermoplastics, thermosets, engineering plastics) required for your application?
- Quality Assurance: What certifications (ISO, FDA, etc.) and quality control processes do they follow?
- Production Volume: Is the company equipped for prototyping, small runs, or large-scale manufacturing?
- Design Support: Do they offer product design, engineering, or prototyping assistance to optimize manufacturability and performance?
- Lead Times and Pricing: Are their turnaround times and costs competitive, transparent, and aligned with your project timeline and budget?
- Sustainability: What commitment does the company have to environmentally responsible manufacturing, recycling, or use of biodegradable plastics?
Looking for a shortlist of trusted plastic forming companies? Compare several plastic forming businesses using our directory, where each profile outlines specialties, experience, and production capabilities. Use our proprietary website previewer to gain insight into each manufacturer’s strengths, then reach out directly for more information or a custom quote using our integrated RFQ form.
Questions to Ask When Evaluating a Plastic Forming Supplier
- What types of plastics and forming processes do you specialize in?
- Can you provide case studies or examples of projects in my industry?
- What is your typical lead time for prototyping and production?
- How do you manage quality assurance and traceability?
- Do you assist with design for manufacturability (DFM) or rapid prototyping?
- What are your minimum order quantities and cost structures?
- Are you equipped to scale from prototyping to mass production?
Ready to Start Your Project?
If you’re ready to bring your plastic product idea to market or need a reliable source for custom plastic fabrication, leverage our directory of vetted plastic forming companies. Request a quote today or consult with our experts to find the perfect manufacturing partner for your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions about Plastic Forming
- What is the difference between injection molding and thermoforming?
Injection molding is ideal for complex, high-volume parts with tight tolerances, while thermoforming is better for large, shallow, or low to medium-volume parts. - Which plastics are suitable for food packaging?
Common food-safe plastics include PET, HDPE, LDPE, and PP, each offering different clarity, barrier, and processability characteristics. - Can plastics be recycled after forming?
Most thermoplastics can be re-melted and recycled, whereas thermosets are generally not recyclable due to their cross-linked structure. - How do I choose the right plastic for my application?
Consider performance requirements (strength, flexibility, temperature resistance), cost, regulatory compliance, and intended use environment. Consult with your plastic forming company for material selection guidance. - What are the lead times for plastic forming projects?
Lead times vary by process (e.g., injection molding tooling vs. vacuum casting) and project complexity. Prototyping may take 1–3 weeks, while production tooling can require 4–8 weeks or more.
Explore More about Plastic Forming and Manufacturing
- What are the latest trends in sustainable plastic manufacturing?
- How does custom plastic fabrication work for unique parts?
- What are the cost factors in plastic molding and forming?
- How do I select the best plastic molding process for my product?
- What quality standards should I look for in a plastic forming company?
- Where can I find expert advice on plastic material selection?
For more information, industry insights, or to begin your project, explore our resources or contact a trusted plastic forming manufacturer today.














 Fiberglass Fabricators
Fiberglass Fabricators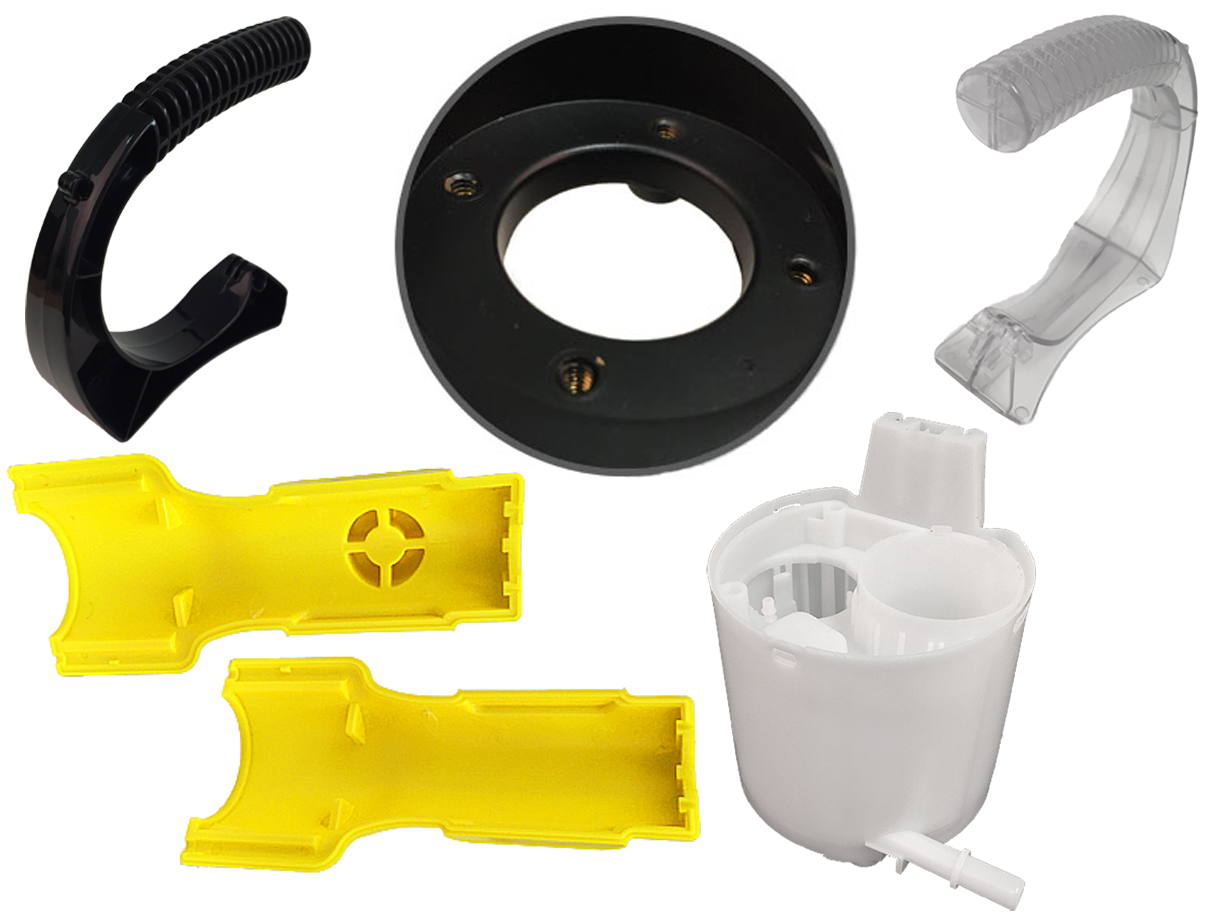 Injection Molded Plastics
Injection Molded Plastics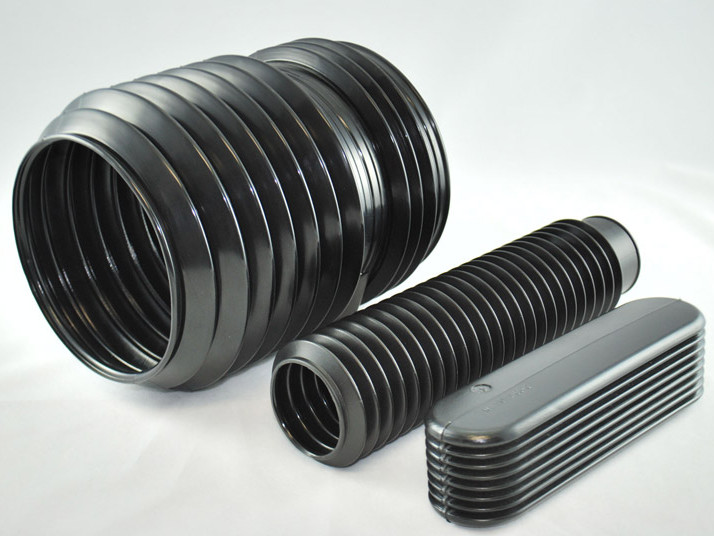 Plastic Blow Molding
Plastic Blow Molding Plastic Dip Molding
Plastic Dip Molding Plastic Extrusions
Plastic Extrusions Plastic Tubing
Plastic Tubing Polyurethane Molding
Polyurethane Molding Rotational Molding
Rotational Molding Vacuum Forming
Vacuum Forming Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services