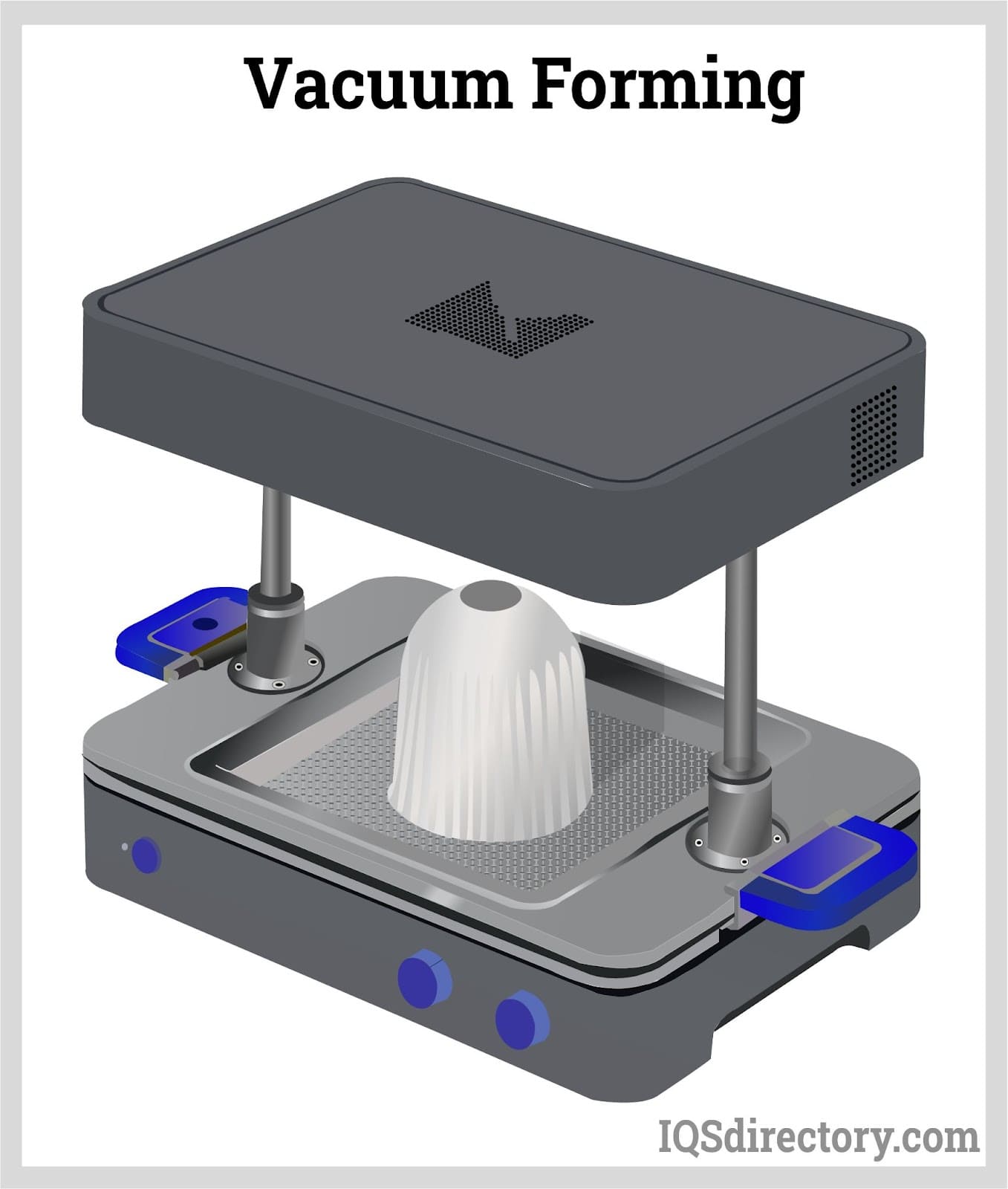
Vacuum forming, also known as thermoforming, vacuum pressure forming or vacuum molding, is a procedure in which a sheet of heated plastic material is shaped a certain way. The mold used to shape the plastic material is also known as a “buck.” Vacuum forming is a type of pressure forming process, and is one of the oldest plastic forming methods. Read More…
Valk’s policy is “to meet or exceed our customer’s requirements, working together as a team with honesty and integrity.” Valk’s success is due to their long standing focus on quality & customer service.

Since 1960, Profile Plastics Inc. has been at the forefront of thermoforming technology. Utilizing the latest software and technology, our expert staff of engineers can design custom vacuum, pressure, and twin-sheet thermoformed solutions. Over the last 60 years, we have developed a process that allows us to deliver consistent, high volume, and precise products with superior quality. Our high...
Quality Plastics & Machine has been a leading manufacturer of vacuum forming since 1976. Whether you need a small batch of custom vacuum-formed parts or a large-scale production run, we have the capabilities and expertise to deliver. We are committed to providing our customers with exceptional vacuum-formed products and services that meet their needs and exceed their expectations. Contact us...

At Arrowhead Plastic Engineering, Inc., we’ve been delivering high-quality vacuum forming solutions since 1972. From concept to production, Arrowhead is with you every step of the way. We can use your 3D CAD model to CNC cut your pattern in house or we can hand sculpt your pattern if a 3D CAD model isn’t available.

Engineered Plastic Products custom forms & fabricates sheet thermoplastic materials, standard & specialized, for any number of industrial & commercial requirements. EPP has been widely recognized for outstanding manufacturing & service since 1958 for companies such as GE, NASA & AT&T. Custom fabricated parts can be as large as 72"x108" down to 2"x2" in any thickness up to 1 1/2". Post-forming...

Brisar Delvco Industries, Inc., specializes in delivering high-quality Thermo & Vacuum forming solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of our clients across a broad spectrum of industries. ISO9001, ISO13485, FDA Registered for Food, Medical Devices & OTC products. In house CNC tooling for quick prototype design, production tools and Thermoformed parts.

At Duo Form, we are pioneers in the realm of vacuum-formed plastic products. With a collective passion for precision engineering and creative problem-solving, we've established ourselves as leaders in delivering high-quality solutions to a wide range of industries.
At Hi-Rel Plastics & Molding, we specialize in precision vacuum forming and thermoforming solutions tailored to meet the unique demands of a wide range of industries. With decades of hands-on experience, we’ve refined our process to deliver high-quality, custom-formed plastic components that meet exacting tolerances and performance standards.

Robinson Industries offers thermoformed and injection molded reusable, heavy duty plastic pallets, packaging and more. We are one of the largest suppliers of reusable pallets to many industries.

More Vacuum Forming Companies
Vacuum Formed Plastic Applications
Vacuum forming, a core thermoforming process, enables manufacturers to efficiently produce a vast range of vacuum-formed plastic components and finished products. By leveraging this highly adaptable plastic fabrication technique, companies across many industries reap the benefits of cost-effectiveness, design flexibility, scalability, and material performance. Are you searching for a versatile manufacturing solution? Explore how vacuum forming can enhance your application.
Industries relying on vacuum forming include telecommunications (for custom housings and infrastructure panels), security (for durable enclosures and shields), cosmetics (for attractive packaging and display trays), automotive (for lightweight body panels and interior trim), appliances (for robust machine covers and parts), medical devices (for sterile packaging and equipment enclosures), electronics (for protective casings and mounting panels), sporting goods (for shell components and gear), and the food and beverage sector (for hygienic packaging and containers). The broad applicability of vacuum forming makes it a go-to choice for both industrial and consumer product manufacturers.
Products Produced from Vacuum Formed Plastics
Vacuum-formed plastic is integral to countless everyday products and specialized solutions, supporting both high-volume and custom manufacturing needs. Its reach extends to:
- Automotive components: bumpers, dashboards, windshields, interior door panels, wheel hub covers, and trunk liners.
- Aerospace and defense: space shuttle interiors, aircraft panels, and drone housings.
- Agricultural equipment: machine panels, seed trays, livestock containers, and irrigation parts.
- Construction: drainpipes, roof lights, window well covers, and insulation panels.
- Consumer products: garden tools, bathtubs, shower surrounds, modular furniture, and household organizers.
- Medical and healthcare: pressure and oxygen masks, prosthetic devices, wheelchair components, dental castings, and medical trays.
- Retail and marketing: point-of-purchase displays, signage, cosmetic trays, and promotional packaging.
- Food service: reusable cutlery, food trays, bakery containers, and beverage cups.
Additionally, vacuum forming is a foundational process for creating plastic packaging that protects, displays, and transports products efficiently. The primary categories of vacuum-formed packaging include blister packs, clamshells, and plastic trays. Each offers unique structural and visual benefits, making them ideal for a range of markets from pharmaceuticals to consumer electronics.
Blister packs are widely used for secure, unit-dose pharmaceutical packaging but also serve in retail for batteries, toys, and hardware. They offer tamper evidence, product visibility, and extend shelf life, making them a preferred choice for compliance and safety.
Clamshell packs are distinct for their hinged, dual-shell design, enveloping and safeguarding products such as electronics, tools, and cosmetics. Their sturdy construction prevents pilferage and damage, while enhancing shelf appeal. If you’re looking for tamper-resistant, secure packaging for high-value retail items, clamshells are often the answer.
Plastic trays—also called blister trays—are shallow, compartmentalized containers used for organizing, displaying, and transporting items. They are indispensable in food service (as food trays and bakery containers), healthcare (for medical device kits), and manufacturing (for parts handling and shipping). Are you seeking efficient ways to package, store, or present your products? Learn more about the right tray design for your application.
History of Vacuum Formed Plastics
The evolution of vacuum forming and thermoforming has deep historical roots. Ancient Romans practiced early forms of material shaping, molding utensils from heated, pliable tortoise shells. This basic concept—heating a material and shaping it over a form—has carried through centuries into today’s advanced plastic fabrication techniques.
The emergence of modern vacuum forming began with John Wesley Hyatt’s invention of celluloid in 1870, the first artificial plastic. Hyatt’s pioneering work in heating and molding this material led to the earliest forms of sheet plastic forming. The 20th century saw rapid advances: during the 1940s and 1950s, vacuum-formed products became essential in retail displays, packaging, and advertising. The introduction of the first commercial thermoforming machines in the 1950s dramatically expanded the scale and precision of plastic part production.
Patent innovations continued: in 1964, the first improved vacuum forming machine for plastic sheets used a combination of vacuum pressure and mold techniques to remove excess air and improve product fidelity. The 1970s saw the arrival of advanced machines with movable heaters, precise vacuum systems, and dynamic molding platforms—laying the groundwork for today’s highly automated, computer-controlled vacuum forming equipment.
Present-day vacuum forming technology leverages a broad spectrum of thermoplastic materials, advanced mold designs, and digital controls. Modern vacuum forming delivers unmatched versatility and efficiency—enabling the mass production of durable, lightweight, and visually appealing plastics for nearly every sector.
Vacuum Formed Plastic Materials Process
The success of any vacuum forming project begins with selecting the right thermoplastic sheet material. Material choice is dictated by the performance requirements, intended use, regulatory standards, and desired aesthetics of the finished product. Common plastics used in vacuum forming include:
- Polyester (PET, PETG): Recyclable, food-safe, and ideal for packaging, bottles, and clear containers.
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): High strength-to-density ratio, excellent for industrial containers, automotive parts, and protective panels.
- LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene): Flexible and tough, used for bags, squeeze bottles, and liners.
- Polypropylene (PP): Resistant to chemicals and heat; used for food containers, medical devices, and automotive components.
- Polystyrene (PS): Economical, available in clear or foamed versions, common in retail trays, packaging, and disposable cutlery.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Impact-resistant and tough, perfect for protective housings, luggage, and panels.
- Acrylics (PMMA): Highly transparent, UV-resistant, used in signage, displays, and lighting covers.
- Polycarbonate (PC): Extremely durable, shatterproof, and transparent; used for safety shields, machine guards, and security glazing.
- Kydex: Specialized PVC/acrylic blend, rigid and chemical-resistant, ideal for holsters, trays, and durable housings.
Want to compare material options for your project? Check our vacuum forming material selector guide.
Polyester
Polyester, especially PET and PETG, is renowned for its clarity, low toxicity, and sustainability. It is widely adopted for food and beverage containers, medical packaging, and retail displays, where transparency and food safety are paramount. PET-based vacuum-formed plastics are easily recyclable, making them a top choice for eco-conscious brands.
HDPE
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is favored for its rigidity, chemical resistance, and durability. Found in milk jugs, detergent bottles, and chemical drums, HDPE’s resilience is offset by its relative difficulty to form at lower temperatures, requiring precise heating control for consistent results.
LDPE
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is flexible yet strong, making it ideal for pliable packaging, squeeze bottles, shrink wraps, and liners. Its resistance to moisture and chemicals makes LDPE a staple in both household and industrial applications.
Polypropylene
Polypropylene is valued for its toughness, fatigue resistance, and ability to withstand autoclaving and chemical exposure. Frequently used in medical packaging, automotive components, and consumer goods, polypropylene’s versatility is matched by its cost-effectiveness in mass production.
Polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a cost-effective, easily vacuum-formed plastic available in both rigid and foamed (Styrofoam) varieties. It is prevalent in disposable products, retail packaging, and lightweight structural applications. However, its environmental impact—due to slow decomposition—makes recycling initiatives increasingly important.
ABS
ABS is an engineering-grade thermoplastic with superior impact strength and dimensional stability. It is tailored for demanding applications, including electronic housings, automotive parts, luggage shells, and consumer goods, where durability and finish quality are essential.
Acrylics
Acrylic plastics offer glass-like clarity and weatherability, making them popular for displays, skylights, and protective screens. Their ability to be colored or tinted expands their use in branded displays and architectural features. While acrylics excel in optical clarity, they are less suited for high-impact or heavy-load applications compared to polycarbonate or ABS.
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate stands out for its unrivaled toughness, light transmission, and heat resistance. It’s a preferred material for security glazing, machine guards, automotive glazing, and aerospace panels. Its ease of thermoforming combined with structural integrity enables intricate, durable designs.
Kydex
Kydex is engineered for applications demanding rigidity, flame resistance, and chemical durability. Its consistent thickness, formability, and range of finishes make it a favorite for transportation interiors, firearm holsters, and utility cases.
Things to Consider When Selecting a Mold Material:
Choosing the right mold material is crucial for achieving optimal results in vacuum forming. Consider these decision factors:
- Rigidity: Does the mold require flexibility for easy release, or must it be rigid for high-precision detail?
- Appearance: Is a flawless surface finish or intricate detail more important than strength or longevity?
- Cost: Evaluate both initial tooling expenses and long-term maintenance or replacement costs. Consider the total cost of ownership for short-run prototypes versus high-volume production.
- Compatibility: Will the mold material withstand the selected plastic’s forming temperatures and potential chemical reactions?
Need help choosing between aluminum, epoxy, wood, or 3D-printed molds? Visit our mold selection guide for vacuum forming.
Vacuum Formed Plastic Process Details
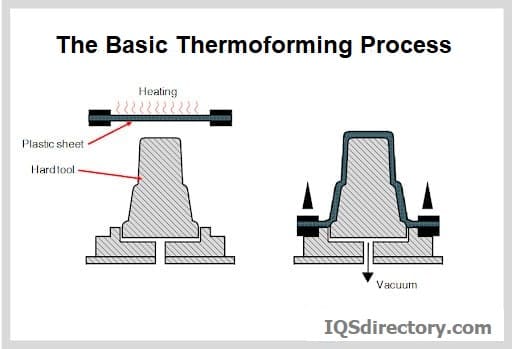
Vacuum forming transforms flat thermoplastic sheets into three-dimensional shapes using heat and vacuum pressure. The typical process includes these eight steps:
- Clamping: The plastic sheet is securely held in a frame, preventing movement during heating and shaping.
- Heating: Radiant or infrared heaters raise the sheet temperature until it becomes pliable.
- Sheet Leveling (Optional): Advanced systems use sensors and air jets to maintain uniform sheet thickness and prevent sagging during heating.
- Pre-Stretching (Bubbling): Some machines inflate the sheet into a bubble to ensure even wall thickness, especially for deep-draw parts.
- Vacuuming: A vacuum pump evacuates air between the sheet and mold, drawing the plastic tightly to the mold surface and capturing fine details.
- Plug Assisting: For complex or deep parts, a plug pushes the sheet into the mold for uniform distribution and sharper definition.
- Cooling and Releasing: Fans or mist sprays accelerate cooling, after which the formed part is released from the mold.
- Finishing: Excess material is trimmed, and secondary operations (drilling, decoration, printing, assembly) are performed to meet final requirements.
Curious about how vacuum forming compares to other plastic fabrication processes like injection molding or blow molding? See our process comparison guide.
Vacuum Formed Plastic Design
Designing for vacuum forming means balancing creativity with manufacturability. Product geometry, wall thickness, draft angles, and undercuts must be considered to ensure smooth forming and easy part release. Customization options such as embossing, engraving, and surface texturing allow brands to add logos, instructions, or decorative features directly into the part. For higher-value products, multi-material assemblies and post-forming assembly can further enhance functionality and appearance.
Have a unique product idea? Contact our experts for vacuum forming design consultation.
Vacuum Formed Plastic Machinery Used
Vacuum Formers
Vacuum forming machines range from compact manual units for prototyping to fully automated, high-capacity production lines. All machines feature integrated heaters (infrared or quartz for rapid response), robust vacuum pumps, and precision temperature controls. Advanced machines may include programmable logic controllers (PLCs), touch-screen interfaces, and sensor-driven feedback for enhanced consistency and efficiency.
Finishing/Trimming Tools and Machinery
Once formed, parts are trimmed and finished using a variety of tools: heated knives, CNC routers, precision saws, punch presses, and roller or guillotine presses. Automated trimming ensures accuracy and repeatability, even for complex geometries or high-volume production runs.
CNC Machines
Computer numerical control (CNC) technology is standard in modern vacuum forming operations. CNC routers and mills enable precise trimming, drilling, slotting, and engraving of formed parts, rivaling the accuracy of injection molding. CNC integration also improves temperature control, cycle time, and quality assurance across batches.
Looking to upgrade your forming operation? Explore the latest in vacuum forming machinery and automation.
Vacuum Formed Plastic Variations and Similar Processes
Twin sheet thermoforming heats and fuses two plastic sheets, creating strong, hollow parts with internal channels. This method is ideal for lightweight, structural applications like pallets, tanks, and double-walled panels.
Vacuum Packaging
Vacuum packaging removes air from within a package, extending shelf life and preventing contamination. This method is widely used in food, medical, and electronics packaging for products requiring airtight, tamper-evident seals. Wondering how vacuum packaging can improve your product’s shelf stability? Learn more about vacuum packaging benefits and techniques.
In-Line Thermoforming/Roll-Fed Thermoforming
These high-output processes continuously feed plastic sheets from a roll or extruder into forming, trimming, and stacking stations. In-line systems are ideal for packaging, food trays, and disposable cups, where speed and efficiency are critical. Roll-fed thermoforming ensures consistent part quality and minimizes material waste.
Basics of Thermoforming
Plastic thermoforming is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the cost-effective shaping of plastic sheets into custom products. Its core advantage lies in flexibility—accommodating simple and complex shapes, short-run prototypes, or mass production. With lower tooling costs compared to injection molding or blow molding, thermoforming is accessible for startups and established brands alike.
The process involves heating a plastic sheet, stretching it over a male (convex) or female (concave) mold, and then cooling it to capture the mold’s shape. Positive (male) tools create interior contours, while negative (female) tools form exterior surfaces. Tooling is typically aluminum or cast resin, balancing cost and durability. Looking for rapid prototyping or low-volume production? Thermoforming’s fast tool lead times and design flexibility make it a smart choice.
Industries that Use Plastic Thermoforming
Home Usage Products
Plastic thermoforming delivers affordable, durable, and customizable solutions for home goods. Modular chairs, tables, storage boxes, and kitchen components are just a few examples. Thermoformed plastics outlast traditional materials, resist moisture, and are easily cleaned—making them ideal for families, renters, and commercial kitchens alike. Considering a switch from wood or metal to plastic for your next home product line? Discover the benefits of thermoformed home products.
Automobile Industry
Lightweight, strong, and design-flexible, thermoformed automotive parts help manufacturers reduce vehicle weight for improved fuel efficiency. Door panels, trim pieces, consoles, battery trays, and underbody covers are routinely made via vacuum forming. For electric vehicles, plastics reduce mass and improve range. Thermoforming also enables rapid model updates and complex geometries, supporting both performance and aesthetics.
Transportation Industry
The transportation sector—encompassing aerospace, rail, marine, and commercial vehicles—demands lightweight, robust components. Thermoformed plastics are used for seat backs, wall panels, luggage bins, windows, and tanks. Their high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and ease of fabrication make them indispensable for reducing fuel consumption and extending service life.
Electronic Casings
From consumer electronics to industrial controls, vacuum-formed plastic casings provide protection, insulation, and sleek aesthetics. Laptops, remote controls, server racks, and modular consoles all benefit from the precision and scalability of thermoforming. As device miniaturization continues, custom plastic enclosures support new product innovations and market trends.
Chemical and Medical Fields
Vacuum-formed plastics excel in medical and laboratory environments, offering sterility, chemical resistance, and disposability. Syringes, pipette tips, sample trays, sterile packaging, PPE, and face shields are all produced via thermoforming. Their consistent quality and regulatory compliance make them vital for healthcare, diagnostics, and research labs. Need high-purity packaging for pharmaceuticals or lab consumables? Explore medical-grade vacuum forming solutions.
Benefits of Vacuum Formed Plastics
Why choose vacuum-formed plastics for your next project? The advantages are compelling:
- Versatility: Suited for both prototyping and high-volume production; can produce anything from simple trays to complex enclosures.
- Design Freedom: Supports intricate shapes, textures, and branding directly on the part surface.
- Cost-Efficiency: Lower tooling and setup costs versus injection molding or die casting.
- Speed: Fast turnaround times from design to finished product; ideal for responding to market shifts or custom orders.
- Material Efficiency: Uses single sheets with minimal waste; excess material can often be recycled.
- Recyclability: Many vacuum-formed plastics are recyclable, supporting sustainability goals.
- Lightweight and Durable: Reduces shipping costs and enhances product performance in demanding environments.
Want to see how vacuum forming compares to other plastic manufacturing processes? View our benefits comparison chart.
How to Choose the Right Vacuum Formed Plastic Manufacturer
Securing the best results from vacuum forming starts with selecting a trusted, experienced manufacturer. Here’s a step-by-step guide to making the right choice:
- Browse reputable vacuum-formed parts manufacturers on our platform; review their capabilities, certifications, and client testimonials.
- Clarify your project requirements: part size, material, tolerances, volume, and finishing needs.
- Request quotes from three to four qualified suppliers; compare pricing, lead times, quality control measures, and customer support.
- Evaluate their technical expertise, in-house design support, and ability to handle secondary operations (trimming, assembly, decorating).
- Choose the partner that best aligns with your quality, budget, and delivery expectations.
Ready to start your project? Connect with leading vacuum forming companies now and bring your product ideas to life!
Frequently Asked Questions About Vacuum Forming
- How does vacuum forming compare to injection molding for cost and quality?
- Which plastics are best for outdoor or UV-resistant vacuum-formed parts?
- Are there sustainable or recycled material options for vacuum forming?
- How fast can I get prototypes using vacuum forming?
- What certifications should I look for in a vacuum forming supplier?
- Can vacuum forming produce custom textures, colors, or branding?
- What maintenance is required for vacuum-formed parts in harsh environments?
- How do I estimate the total cost of a vacuum forming project?
Start Your Vacuum Forming Project Today
Whether you need rapid prototyping, high-volume production, or customized solutions, vacuum forming delivers unmatched value. Harness the benefits of advanced thermoplastic materials, flexible design, and streamlined manufacturing for your next application. Contact our team to discuss your requirements, request samples, or schedule a design consultation. Empower your business with the versatility and efficiency of vacuum-formed plastics.






 Fiberglass Fabricators
Fiberglass Fabricators Injection Molded Plastics
Injection Molded Plastics Plastic Blow Molding
Plastic Blow Molding Plastic Dip Molding
Plastic Dip Molding Plastic Extrusions
Plastic Extrusions Plastic Tubing
Plastic Tubing Polyurethane Molding
Polyurethane Molding Rotational Molding
Rotational Molding Vacuum Forming
Vacuum Forming Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services